这将是我搬家之前的最后一次发文了。
没学过公司金融,对资本定价这一块我确实一点概念都没有,需要多花点时间。
Corporate Finance 经典教材 Ross 《公司理财》(国内翻译成公司理财,和公司金融是一回事)

资本资产定价-现代金融学核心
- 系统性风险 (大家都没办法规避的风险)
- 非系统性风险
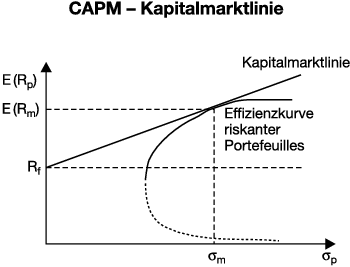
CAPM模型 Capital Asset Pricing Model 拿过诺贝尔经济学奖
风险资产预期收益率=无风险收益率+风险议价(risk premium)
CAPM is widely used throughout finance for the pricing of risky securities, generating expected returns for assets given the risk of those assets and calculating
costs of capital.

我觉得这个公式还是很好理解的,把无风险收益率移到公式左边,就能清楚看到资产预期收益率和市场预期收益率之间的关系了。多个风险资产加上权重,就形成了风险资产组合。
CAPM 运算举例:我们来算一个股票的预期收益率。设定无风险收益率是2%,股票系数beta (risk measrue)为2,在此时间区间内市场预期收益率为10%。这样我们就算出这只股票预期收益率为18%。
2% + 2*(10%-2%) = 18%
股票定价
实体资产定价= 成本(会计成本)+利润(机会成本)
金融资产定价= 会计成本 + 机会成本
- 绝对定价法
DCF模型 不用回顾了,任何一门课都会讲到。
盈利预测主观性很强
机会成本怎么算,用CAPM 和 WACC
Weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is a calculation of a firm’s cost of capital in which each category of capital is proportionately weighted.
All sources of capital, including common stock, preferred stock, bonds and any other long-term debt, are included in a WACC calculation. An increase in WACC denotes
a decrease in valuation and an increase in risk.
- 相对定价法
按照参考系对资本定价
倍数Multiples=公司价值/利润表内指标(或是资产指标)
PE倍数,P denotes Price, E denotes Earnings
The price-earning ratio (P/E Ratio) is the ratio for valuing a company that measures its current share price relative to its per-share earnings.
The price earnings ratio can be calculated as: Market Value per Share / Earnings per Share
打个比方说一个公司现在的股价是43块,在过去的12个月它的盈利是1.95每股。这样它的PE指数就是43除以1.95,即22.05。
PS指标 Price-To-Sales Ratio
债券定价
主要使用DCF模型
一年期以内叫T-Bill
十年期以内叫Note
十年期以上才叫Bond
具体区别是
Treasury bills, notes and bonds are marketable securities the US government sells in order to pay off maturing debt and to raise the cash needed to run the federal
government. When you buy one of these securities, you are lending your money to the government of the United States.
T-bills are short-term obligations issued with a term of one year or less, and because they are sold at a discount from face value, they do not pay interest
before maturity. The interest is the difference between the purchase price and the price paid either at maturity (face value) or the price of the bill sold prior to maturity.
Treasury notes and bonds, on the other hand, are securities that have a stated interest rate that is paid semi-annually until maturity, What makes notes and bonds
different are the terms to maturity. Notes are issued in two-, three-, five- and 10-year terms. Conversely, bonds are long-term investments with terms of more than 10 years.
平价发行,溢价发行,折价发行
新闻里提到的:债券收益率上升(市场机会成本,市场通行利率),利率上升,债券价格下跌。债券收益率下降,利率下降,债券价格上涨。


Kommentar schreiben